Change Language :
iglidur® J2 - Material data
Material table
General specification
Unit
iglidur® J2
Test method
density
g/cm³
1,44
Colour
light yellow
max. Moisture absorption at 23°C/50% room humidity.
% by weight
0,2
DIN 53495
max. total moisture absorption
wt.-%
1,3
Sliding friction coefficient, dynamic, against steel
µ
0,11 - 0,27
pv value, max. (dry)
MPa x m/s
0,23
Mechanical specification
flexural modulus
MPa
3.605
DIN 53457
flexural strength at 20°C
MPa
101
DIN 53452
Compressive strength
MPa
77
maximum recommended surface pressure (20°C)
MPa
46
Shore D hardness
n.b.
DIN 53505
Physical and thermal specification
Upper long-term application temperature
°C
+90
upper short-term application temperature
°C
+110
Lower application temperature
°C
-50
thermal conductivity
[W/m x K]
0,25
ASTM C 177
coefficient of thermal expansion (at 23°C)
[K-1 x 10-5]
7
DIN 53752
Electrical specification
Volume resistivity
Ωcm
> 1013
DIN IEC 93
surface resistance
Ω
> 1012
DIN 53482
Table 01: Material data
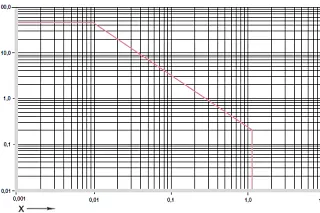
diagram. 01: Permissible pv value for iglidur® J2 plain bearings with 1 mm wall thickness in dry operation against a steel shaft, at +20 °C, installed in a steel housing
X = surface speed [m/s]
Y = load [MPa]
iglidur® J2 is directly comparable with our classic iglidur® J in terms of the general mechanical and thermal specification. However, iglidur® J2 is superior to iglidur® J in terms of mechanical specifications, such as maximum recommended surface pressure. However, the wear resistance in dry operation is inferior.
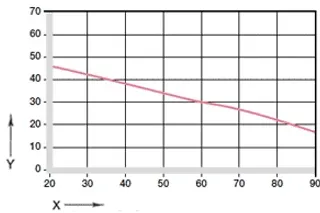
diagram. 02: maximum recommended surface pressure as a function of temperature (46 MPa at +20 °C)
X = temperature [°C]
Y = load [MPa]
Mechanical specification
The compressive strength of iglidur® J2 plain bearings decreases with increasing temperatures. diagram. 02 illustrates this correlation. The maximum recommended surface pressure represents a mechanical material parameter. Conclusions on the tribology cannot be drawn from this.
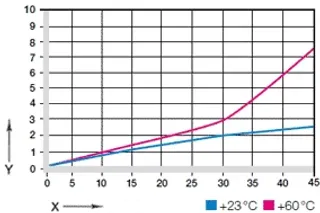
Diagram 03: Deformation under pressure and temperature
X = load [MPa]
Y = Deformation [%]
diagram. 03 shows the elastic deformation of iglidur® J2 under radial load. Possible plastic deformation depends, among other things, on the duration of the load.
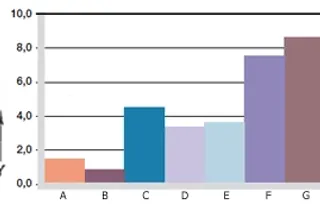
diagram. 06: Wear, rotating application with subdl. shaft materials, p = 1MPa, v = 0.3m/s
X = Shaft material
Y = wear [μm/km]
A = aluminium, hard anodised
B = free cutting steel
C = Cf53
D = Cf53, hard chrome-plated
E = HR carbon steel
F = 304 SS
G = high grade steel
Shaft materials
Friction and wear are also highly dependent on the mating partner. Shafts that are too smooth increase both the coefficient of friction and the wear of the bearing. diagram. 06 shows an extension of the results of tests with different shaft materials. In diagram. 06 it can be seen that iglidur® J2 delivers good wear values in rotation at 1 MPa, especially with free cutting steel. In dry running, the wear values on other shaft materials are significantly higher in some cases.
In contrast to many other iglidur®materials, the wear rate in swivelling is slightly higher compared to rotation with otherwise identical parameters (diagram 07).
Consulting
I look forward to answering your questions

igus Australia1300 726 244Write e-mail
Shipping and consultation
In person:
Monday to Friday from 8 am - 5 pm.



