Change Language :
iglidur® F - Material data
Material table
General specifications
Unit
iglidur® F
Test method
Density
g/cm³
1.25
Colour
black
Max. total moisture absorption at 23°C/50% room humidity
% weight
1.8
DIN 53495
Max. total moisture absorption
% weight
8.4
Sliding friction coefficient, dynamic, against steel
µ
0.1 - 0.39
pv value, max. (dry)
MPa x m/s
0.34
Mechanical specifications
Elastic modulus
MPa
11.600
DIN 53457
Flexural strength at 20°C
MPa
260
DIN 53452
Compressive strength
MPa
98
Maximum recommended surface pressure (20°C)
MPa
105
Shore D hardness
84
DIN 53505
Physical and thermal specifications
Upper long-term application temperature
°C
+140
Upper short-term application temperature
°C
+180
Lower application temperature
°C
-40
Thermal conductivity
[W/m x K]
0.65
ASTM C 177
Coefficient of thermal expansion (at 23°C)
[K-1 x 10-5]
12
DIN 53752
Electrical specifications
Specific transitional resistance
Ωcm
< 103
DIN IEC 93
Surface resistance
Ω
< 102
DIN 53482
Table 01: Material data
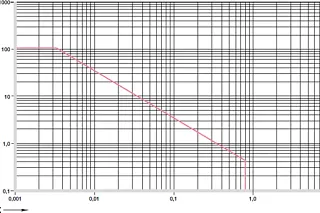
Diagram 01: Permissible pv values for iglidur® F plain bearings with 1mm wall thickness in dry operation against a steel shaft, at +20°C, installed in a steel housing
X = surface speed [m/s]
Y = pressure [MPa]
When plain bearings need to be electrically conductive, especially in applications that should keep out static, iglidur® F is the right choice. Moreover, the iglidur® F plain bearings are extremely pressure-resistant. At room temperature, they could be statically loaded up to 100MPa.
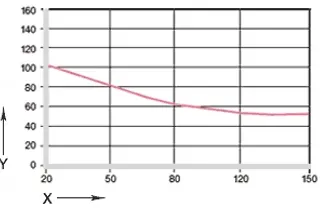
Diagram 02: Maximum recommended surface pressure as a function of temperature (105MPa at +20°C)
X = temperature [°C]
Y = pressure [MPa]
Mechanical specifications
The maximum recommended surface pressure represents a mechanical material parameter. Conclusions on the tribology cannot be drawn from this. The compressive strength of iglidur® F plain bearings decreases with increasing temperatures. Diagram 02 illustrates this correlation. At the long-term permissible application temperature of +140°C, the permissible surface pressure is still 50MPa.
Diagram 03 shows the elastic deformation of iglidur® F under radial loads. Under the maximum recommended surface pressure of 105MPa, the deformation is less than 3.0%. Plastic deformation can be negligible up to this compressive load. However, it also depends on the duration of exposure.
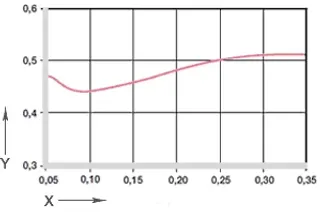
Diagram 04: Coefficient of friction as a function of the surface speed, p = 0.75MPa
X = surface speed [m/s]
Y = coefficient of friction μ
Friction and wear
The coefficients of friction in dry operation are not as favourable with iglidur® F plain bearings as with various other iglidur® materials. However, iglidur® plain bearings can be lubricated without hesitation, and iglidur® F plain bearings achieve excellent results in the comparison of lubricated iglidur® bearings with each other.
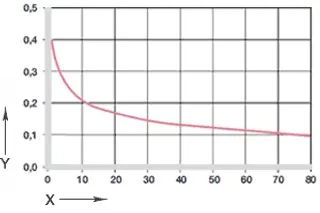
Diagram 05: Coefficients of friction as a function of the load, v = 0.01m/s
X = load [MPa]
Y = coefficient of friction μ
iglidur® F
Dry
Grease
Oil
Water
Coefficients of friction µ
0.1 - 0.39
0.09
0.04
0.04
Table 04: Coefficients of friction for iglidur® F against steel (Ra = 1μm, 50HRC)
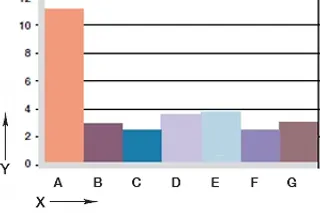
Diagram 06: Wear, rotating application with different shaft materials, p = 1MPa, v = 0.3m/s
X = shaft material
Y = wear [μm/km]
A = Aluminium, hard-anodised
B = free cutting steel
C = Cf53
D = Cf53, hard-chromed
E = HR carbon steel
F = 304 stainless steel
G = high grade steel
Shaft materials
Diagrams 06 and 07 show an excerpt of the results of tests with different shaft materials that were carried out with plain bearings made of iglidur® F. In the lowest load range, the hard-chrome plated shaft proves to be the most favourable mating partner in rotating applications with iglidur® F plain bearings.
Consulting
I look forward to answering your questions

igus Australia1300 726 244Write e-mail
Shipping and consultation
In person:
Monday to Friday from 8 am - 5 pm.


